7 Reasons GPS Tracking Can Be Wrong (And How to Fix It)
GPS tracking has revolutionized fleet management, personal safety, and logistics. But even the best systems can show wrong locations, delayed updates, or complete signal loss. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common causes of GPS tracking errors—and practical ways to improve accuracy.

1. Satellite Signal Obstruction
Tall buildings, tunnels, dense forests, and even heavy cloud cover can block or reflect GPS signals—a phenomenon known as “multipath error.” This is especially common in urban areas (called the “urban canyon” effect).

How to improve it:
- Use GPS devices with GLONASS or Galileo support (multi-constellation receivers).
- Install antennas with a clear view of the sky.
- In vehicles, mount trackers on the windshield or roof—not under metal surfaces.
2. Low Battery or Power Issues
When a GPS tracker’s battery is low, it may reduce update frequency or shut down non-essential functions—including GPS signal processing.

How to improve it:
- Use hardwired trackers for vehicles (connected to the OBD-II port or main battery).
- Set up low-battery alerts in your tracking platform.
- Choose devices with power-saving modes that still maintain location accuracy.
3. Atmospheric Interference
Solar flares, ionospheric delays, and geomagnetic storms can distort signals between satellites and your device—especially during high solar activity.
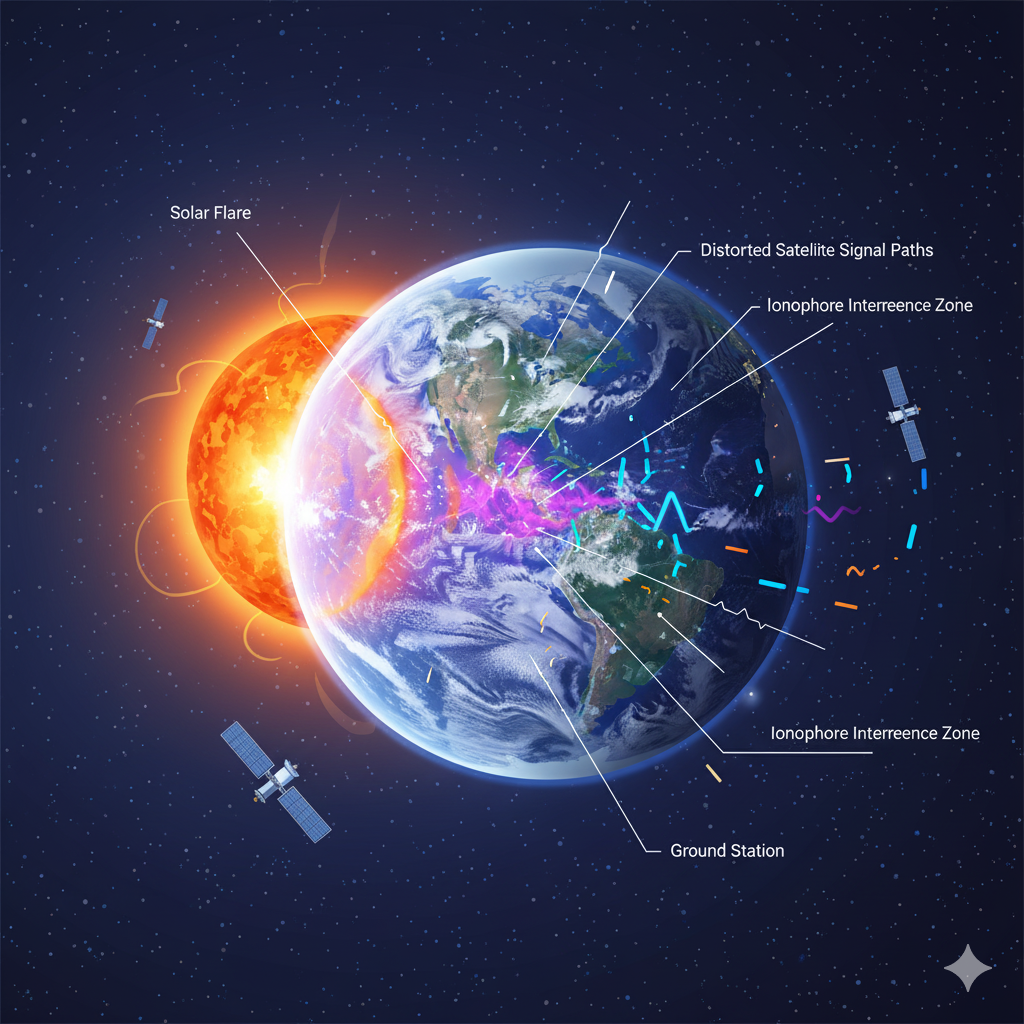
How to improve it:
- Use GPS systems with WAAS (Wide Area Augmentation System) or DGPS (Differential GPS) for real-time corrections.
- Check space weather forecasts if precision is critical (e.g., surveying, aviation).
4. Poor Device Quality or Outdated Firmware
Cheap or outdated GPS trackers often use low-sensitivity receivers that struggle in weak-signal areas.
How to improve it:
- Invest in industrial-grade trackers from reputable brands.
- Regularly update firmware to fix bugs and improve signal processing.
5. Incorrect Installation
Metal surfaces, electronic interference (from radios, inverters), or improper grounding can disrupt GPS performance.
How to improve it:
- Follow manufacturer installation guidelines.
- Avoid placing trackers near high-power electronics.
6. Software or Server Delays
Sometimes the GPS device works fine—but the tracking platform delays updates due to server load or poor internet connectivity.
How to improve it:
- Choose a tracking provider with robust cloud infrastructure (like SatellitalTracking.com).
- Ensure your device uses cellular networks with strong local coverage (4G/LTE preferred).
7. User Error or Misconfiguration
Incorrect geofence settings, wrong time zones, or disabled location services can create false alerts or missing data.
How to improve it:
- Train users on proper system setup.
- Use platforms with intuitive dashboards and real-time diagnostics.
Final Thoughts: Accuracy Is Achievable
While no GPS system is 100% perfect, understanding these common pitfalls—and applying the right fixes—can dramatically improve reliability. Whether you’re managing a fleet in Mexico City, tracking assets in Texas, or monitoring personal devices across Latin America, precision starts with the right hardware, installation, and platform.
Need help choosing the right GPS tracking solution for your region? Explore our services or contact our team today.
